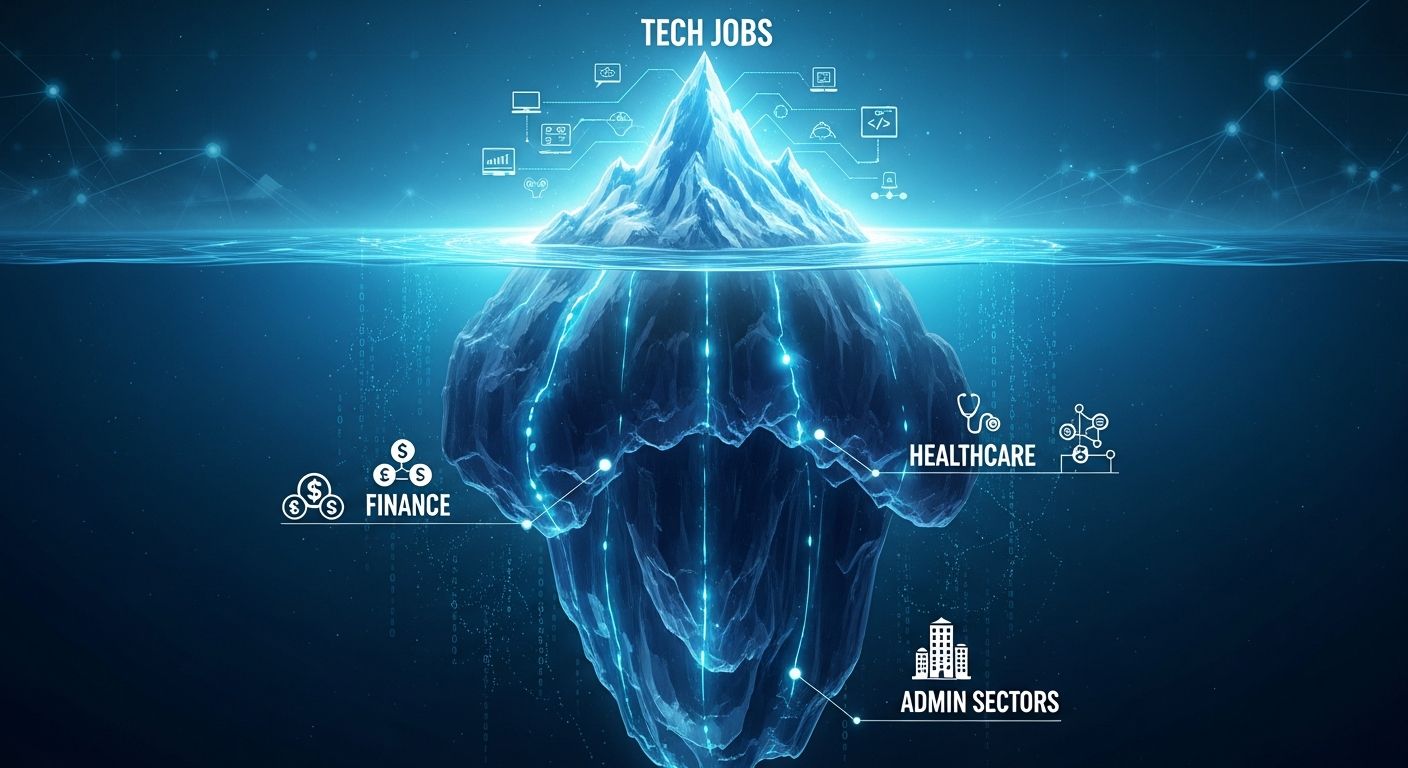
Introduction: AI's Hidden Impact on the Workforce
A recent study released by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has unveiled a detailed and quantifiable scenario regarding the future of employment. According to the findings, artificial intelligence already possesses the capabilities to replace approximately 11.7% of the U.S. workforce. This percentage translates into a colossal economic impact, affecting wages totaling $1.2 trillion. The research relies on an advanced simulation tool called the Iceberg Index, which offers a precise map of technological disruption, drilling down to the zip code level.
The Iceberg Index represents a breakthrough for lawmakers and businesses, providing crucial data to plan billion-dollar investments in reskilling and training, anticipating changes before they manifest in the real economy.
What is the Iceberg Index and How Does It Work?
The study was made possible through a collaboration between MIT and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). Researchers created what they call a "digital twin" of the U.S. labor market. This tool simulates the interactions of 151 million workers across the country, analyzing how they are affected by AI adoption and corresponding policies.
"Basically, we are creating a digital twin for the U.S. labor market."
Prasanna Balaprakash, ORNL Director and research co-leader
The model treats each worker as an individual agent, tagged with specific skills, tasks, occupation, and location. By mapping over 32,000 skills across 923 occupations in 3,000 counties, the index measures where current AI systems can already perform those tasks.
Beyond the Tip of the Iceberg: At-Risk Sectors
One of the most surprising results of the study concerns the discrepancy between public perception and data reality. Layoffs and role shifts in the tech and IT sectors — often the focus of news — represent just the "tip of the iceberg," accounting for merely 2.2% of total wage exposure (about $211 billion).
Beneath the surface, the Iceberg Index reveals that the majority of the impact (the remaining $1.2 trillion in wages) hits routine functions often overlooked in automation forecasts, including:
- Human Resources
- Logistics
- Finance
- Office Administration
- Professional Services and Healthcare
Geographic Impact: Not Just Silicon Valley
The index challenges the common assumption that AI risk is confined to coastal tech hubs. Simulations show that exposed occupations are spread across all 50 states, including inland and rural regions often left out of the technological innovation conversation.
"Project Iceberg enables policymakers and business leaders to identify exposure hotspots, prioritize training and infrastructure investments, and test interventions before committing billions to implementation."
Iceberg Project Report
A "Sandbox" for Labor Policy
Rather than just a prediction engine for job losses, researchers position the Iceberg Index as an interactive simulation environment ("sandbox"). States like Tennessee, North Carolina, and Utah have already begun using the platform to validate their own data and build proactive policy scenarios.
North Carolina State Senator DeAndrea Salvador highlighted the importance of being able to drill down to local details, analyzing data at the county level to understand how automation might affect local GDP and employment.
Conclusion
While sectors like healthcare, nuclear energy, and manufacturing maintain some protection due to the physical nature of the work, the future challenge will be integrating technologies like robotics and AI assistants to strengthen these industries rather than hollow them out. The Iceberg Index serves as an essential tool for navigating this transition.
FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some quick answers based on data from the Iceberg Index and the MIT study.
What is the Iceberg Index?
It is a labor simulation tool created by MIT and ORNL that acts as a digital twin of the US market to map the impact of AI.
Which sectors are most at risk according to the MIT study?
Beyond tech, AI heavily impacts finance, healthcare, human resources, logistics, and office administration.
Will AI really replace human jobs?
The study indicates that AI can already perform tasks equivalent to 11.7% of the labor market, but the goal is to guide reskilling rather than just predicting layoffs.
Does AI impact only major tech cities?
No, the Iceberg Index shows that AI exposure is widespread across all 50 states, including rural and inland areas.
How can governments use this data?
Lawmakers can use the index to simulate "what-if" scenarios and test the effectiveness of training investments before implementing them.